
Detox from the harmful effects of alcohol !
The consumption of alcohol exposes our bodies to many toxic molecules, known as xenobiotics, of which acetaldehyde is one. Acetaldehyde is a by-product of the elimination process of alcohol. It is responsible for a significant oxidising effect leading to numerous cellular damages. Indeed, this alcohol metabolite also interacts with DNA and causes damage to the genetic material. In the long term, alcohol consumption favours the development of cardiovascular diseases (arrhythmia, hypertension, etc.) and the appearance of cognitive disorders. In the gastrointestinal tract, alcohol irritates the mucous membranes of the stomach and esophagus and leads to an accumulation of fatty acids that clogs the liver: this is called hepatic steatosis. The liver is the main organ involved in the elimination of toxic compounds, so detoxification is essential to help the liver cells when alcohol is consumed.
The liver: the organ of alcohol metabolism
The process of eliminating alcohol involves several liver enzymes.
- Alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase
Firstly, alcohol is taken over by the enzyme pair ADH (alcohol dehydrogenase) / ALDH (aldehyde dehydrogenase). ADH first metabolises the alcohol (ethanol) into acetaldehyde. ALDH then converts the latter into acetic acid, which is broken down into water and CO2 before being eliminated via respiration. Furthermore, the low expression of one form of ALDH, ALDH2, particularly in certain Asian populations, leads to the accumulation of acetaldehyde in the body, a phenomenon that can cause even greater damage.
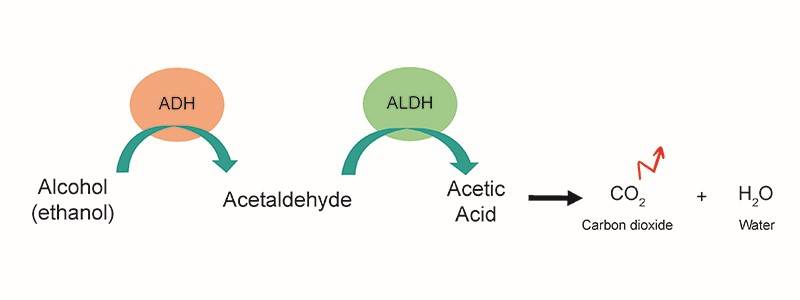 Some amino acids such as L-arginine are able to induce ADH and ALDH activity to facilitate the elimination of acetaldehyde.
Some amino acids such as L-arginine are able to induce ADH and ALDH activity to facilitate the elimination of acetaldehyde.
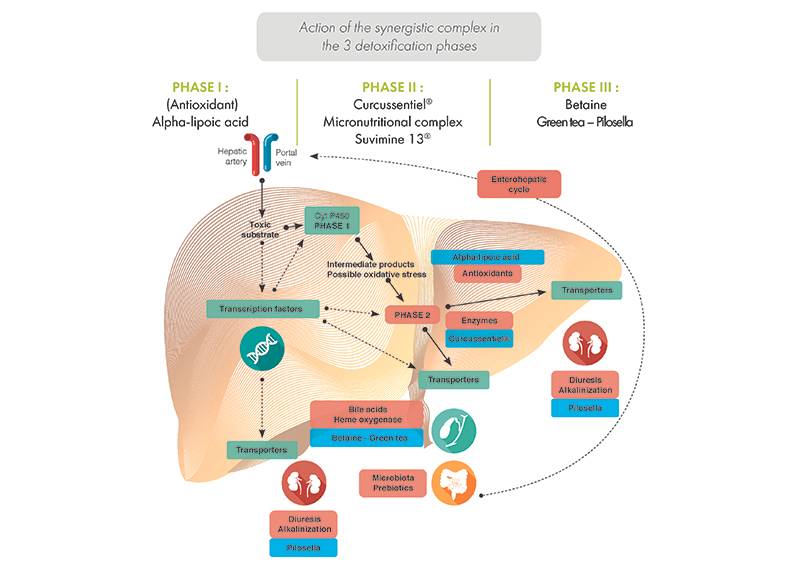
The metabolism of xenobiotics also involves other steps, divided into three phases. Phases 1 and 2 correspond to the xenobiotic neutralisation phases, while phase 3 allows the elimination of xenobiotics via the kidney and intestine.
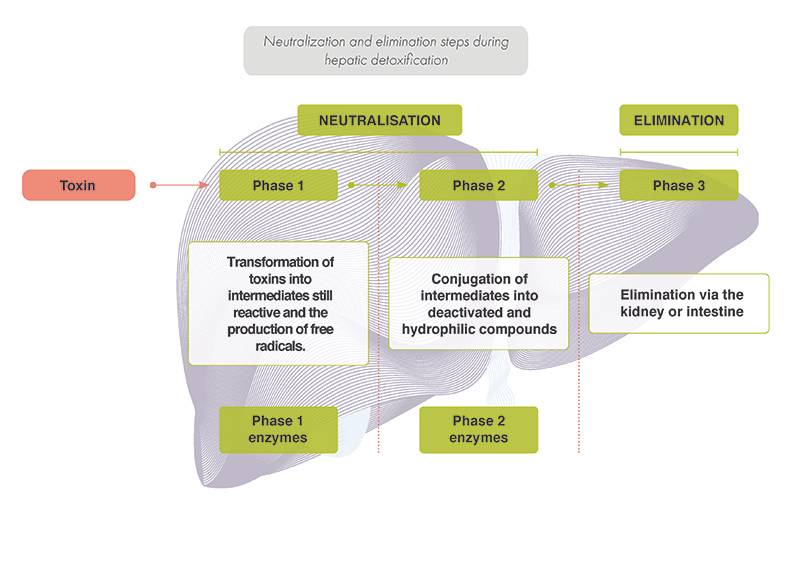
- Phase 1: Cytochromes P450
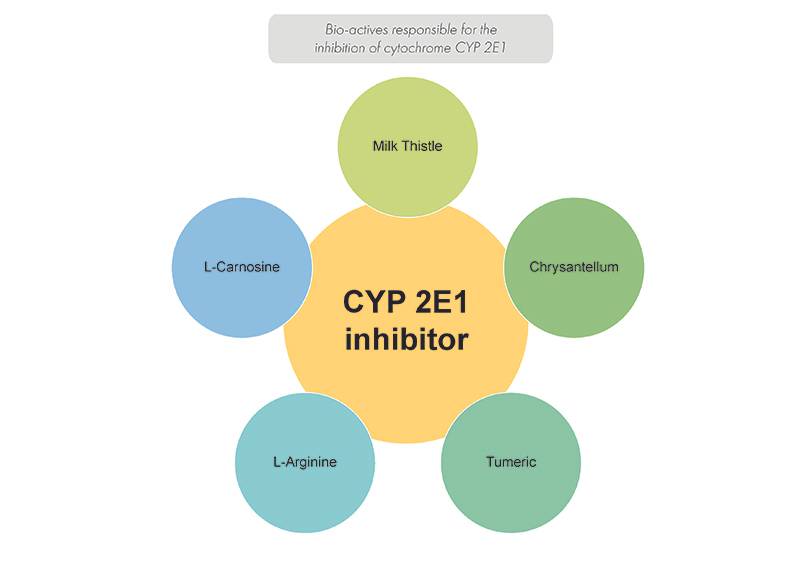
These enzymes neutralise toxic compounds, while producing pro-oxidant reaction intermediates in return. Some compounds are able to limit the production of free radicals, responsible for oxidative stress, by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for their production: the cytochrome CYP 2E1. Inhibition of CYP 2E1 thus favours the handling of alcohol by the ADH/ALDH enzymatic couple mentioned above. These compounds include turmeric, milk thistle and chrysantellum, but also L-arginine and L-carnosine.
- Phase 2: Glutathione-S-Transferase and Sulpho-transferases
Following phase 1, phase 2 enzymes take over the metabolites produced and attach small chemical groups to them in order to modify the solubility of the toxins and facilitate their elimination. This is the "conjugation" mechanism. In the alcohol detoxification process, the conjugated molecules correspond to sulphate groups added by Sulpho-transferases (SULTs), and to glutathione attached by the phase 2 enzyme Glutathione-S-Transferase (GST).
It is therefore important to be able to induce the activity of these enzymes to facilitate the elimination of toxic compounds, particularly with turmeric. In addition, the contribution of N-acetylcysteine, a precursor of glutathione, ensures the proper functioning of GST. The action of N-acetylcysteine is complementary to that of alpha-lipoic acid, which regenerates the antioxidant character of glutathione, as well as to that of selenium, a cofactor of the GSTs and a trace element that is essential to their functioning.
- Phase 3: Elimination from the body
This phase consists of the elimination of toxic substances from the body through the urine or faeces. It requires an alkalinization of the pH (increase of the pH) and the increase of the diuresis, volume of urinary secretion, thanks to the pilosella. In addition, a good balance of bile acids and an increase in their secretion are essential. This balance and this increase are notably ensured by betaine, chrysantellum, green tea, milk thistle and turmeric.
Oxidative stress and liver protection during alcohol detoxification
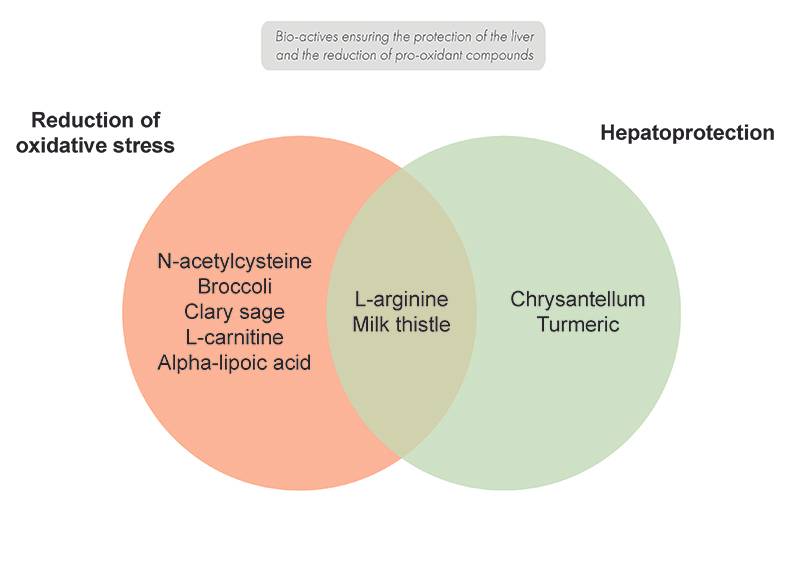
In the context of an alcohol detox, it is essential to combat oxidative stress and to exert a hepatoprotective effect with N-acetylcysteine, milk thistle, broccoli, clary sage, chrysantellum and turmeric, but also with L-carnitine, L-arginine, and alpha-lipoic acid.
A complete detox complement
To detoxify one's organism following the consumption of alcohol, DETOXSSENTIEL Alcohol provides a synergistic complex. DETOXSSENTIEL Alcohol is composed of brown capsules containing: alpha-lipoic acid, betaine, turmeric extract titrated in curcumin, pilosella extract, green tea extract titrated in polyphenols, as well as our micronutritional complex Suvimine 13® containing selenium, zinc, and 11 vitamins, including vitamins of the B group, vitamin C, and natural vitamin D3 and E. The curcumin in our Curcussentiel® active ingredient is microencapsulated in soluble galactomannan fibres derived from fenugreek, making it 270 times more bioavailable than a standard turmeric extract. Our curcumin is also combined with ginger extract titrated in gingerol to facilitate its absorption.
The white capsules and the sachet of DETOXSSENTIEL Alcohol participate in the specific action of the enzymes directly involved in the elimination of acetaldehyde, thanks to N-acetylcysteine, L-arginine and L-carnosine, as well as clary sage, chrysantellum extract titrated in flavonoids and milk thistle extract titrated in silymarin.
1 day of detox with DETOXSSENTIEL Alcool corresponds to taking 3 brown capsules, 1 white capsule and 1 sachet. DETOXSSENTIEL Alcool is taken 1 day out of 2 during chronic consumption, or 1 day after any significant alcohol consumption.
Alcohol abuse is dangerous for your health. DETOXSSENTIEL Alcool does not affect the alcohol level in the blood.











